Feature your business, services, products, events & news. Submit Website.
Breaking Top Featured Content:
The Evolution of Crypto Fundraising: IDO as an Alternative?


IDO (Initial Dex Offering) is a new crowdfunding model in the crypto market that became quite popular in early 2021 amid growing interest in DeFi. Therefore, it’s time to tell how this works, how it differs from both ICO and IEO. It is also worth pointing out the pros and cons of IDO, as well as evaluating the possibilities of the new crowdsale method.
Prehistory
The first ICO (Initial Coin Offering) was held by the Mastercoin protocol in 2013. In 2017–2018, the popularity of ICOs was high — in 2017, projects raised $5.6 billion, and in the first quarter of 2018 — $3.3 billion. Under the ICO model, anyone could start selling their tokens to everyone. At the same time, the token issuer does not need to disclose his identification data, nor present the MVP, nor confirm qualifications, nor in any other way, prove that issuer is a reliable developer, and his project is a profitable investment. It was enough just to create a smart contract to sell your tokens for bitcoins or ether. Such easy access to investments attracted interest and money to the ICO market, but at the same time, the lack of any control and requirements also became the main reason for the increase in the number of scammers. So, according to a study by Satis Group LLC, in 2018, more than 80% of all token sales in the ICO market were scams. When investors realized this problem, they began to involve regulators and sue token sellers and even those who advertised these projects as well.
By the end of 2018, the ICO had exhausted, so crypto exchanges offered an alternative to ICO — Initial Exchange Offering (IEO). In 2019, IEOs were replaced by IDOs: in June 2019, the Raven Protocol project placed tokens on Binance DEX. What are the differences between these methods of raising funds? During the ICO, the issuer independently chooses the exchanges and agrees on the placement of tokens. With IEO, funds are raised by a centralized platform like Binance and FTX, and with IDO, by a decentralized exchange like Binance DEX and Uniswap. For ICO and IEO, projects pay listing fees. DEX does not charge listing fees. While an IPO is the standard model for raising capital in the stock markets, the crypto market is increasingly mobile. We can call this the evolution of crypto crowdfunding.
High costs, the inability to trade on other exchanges, and often not transparent requirements for projects became the reason that many developers did not like the IEO. In addition, both startups and investors did not like IEO’s dependence on centralized exchanges, which goes against the idea of crypto and blockchain — decentralization. In order to neutralize all these shortcomings, it was decided to do the same, but on decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges (DEX). This is how the IDO tool appeared. It assumes that any DEX user can run their own IDO. You just need to activate the corresponding smart contract, register a new token and provide the pool with liquidity.
Over the past year, the number of funds blocked in DeFi has grown 67 times. According to the DeFi Pulse service, at its peak on May 12, 2021, this figure reached $89 billion, now it is $67 billion. This indicates that decentralized services are becoming more widespread. In 2020, interest in DeFi has skyrocketed. As a result, a new way of attracting funds- IDO, began to gain popularity. Projects issue tokens that are already backed by liquidity pools on DEX. In order to participate in the IDO, investors need to register in the whitelist in advance. One of the most popular IDO platforms is Coinlist and many others. If we are talking about projects on Ethereum, then, most often, their token sales are held on decentralized crypto exchanges as Uniswap. IDO is a new way to attract funding, which, unlike ICO and IEO, does not have clear rules. It all depends on the issuer of the token. Tokens that are issued during the IDO are guaranteed to be placed on a decentralized crypto exchange. This was one of the main problems of the ICO, many of which never made it to listing on a centralized platform. The most profitable IDO at the moment is Flow from the Dapper Labs project. At its peak, its value rose 433 times from the initial placement. IDO isn’t just about DeFi companies. For example, the crypto payment company CoinsPaid — in 2020 grew x5, due to which it began to process 5% of all transactions in the bitcoin network. Listing a token on a DEX does not guarantee the growth of its quotes. IDO has high risks, this must be taken into account when deciding to participate in the token sale as well.
What is IDO?
There is no official definition of IDO. Some community members refer to this concept as an acronym for Initial DEX Offering. This could indicate any form of token offering that is DEX-related or not at all. IDO is a fundraising method in which crowdsale is carried out through a DEX using liquidity pools through which traders can easily and quickly buy new tokens on the DEX. The liquidity pool is the trading pairs of common cryptocurrencies and stable coins, for example, USDT/ETH. Thanks to them, traders can quickly switch between crypto-assets and stable coins depending on market conditions. And since the volatility of stablecoins is negligible, it reduces the risks of losing your investments due to the extreme volatility of the crypto market. At the same time, like ICOs, IDOs have minimum requirements for investors and developers (often, there are none at all). Because of this, this method of raising funds has become very popular among DeFi projects in 2020. And if the regulator does not intervene again, then, most likely, IDO will become a new trend in the world of cryptocurrencies.
The IDO is fully and independently organized by the token issuer, so anyone can organize it if they want to choose a similar form of token distribution. This action is 100% organized by the issuer with the project’s own IT system or online within the blockchain using transactions from the project or the issuer. The IDO is not controlled by others. Since an IDO can be carried out by anyone, technically, it should be regulated by the jurisdiction of the issuer, but it depends entirely on the token issuer itself and does not provide any guarantees. So this fundraising depends entirely on the team. IDO pricing is also determined by the team. Price can have its own logic, regardless of whether someone agrees with it or not, and it does not matter if such a price reflects the real usability of the token. Also, the project team independently determines whether KYC is required during the IDO. This factor is a risk if the project team for the free participation of investors, but the presence of KYC is also not a guarantee against failure today.
Table. Features of crypto fundraising
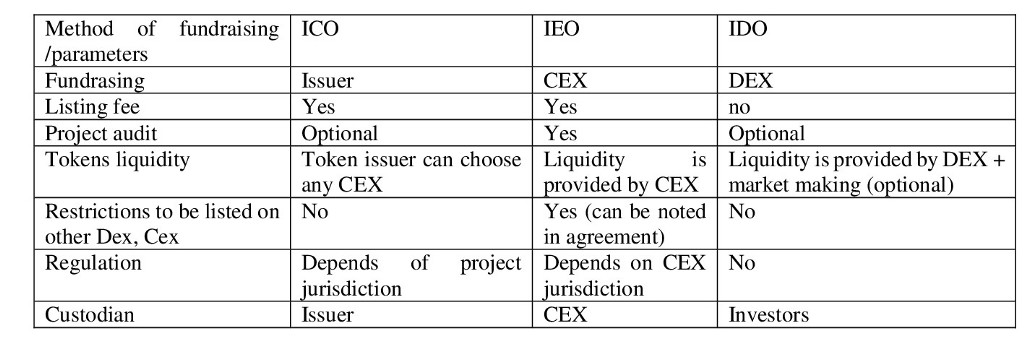
During the IDO, you need to protect investors from scammers. More often, scammers create and publish fake token sale contracts. The project should make IDO as transparent as possible: publish the address on the website and in social networks, as well as delete messages with fake addresses from fake accounts. Additionally, projects can use popular DeFi solutions to optimize the investment interest in the project, such as optimizing payment processing and launching staking if desired. But in fact, preparing and conducting an IDO is not at all easier than an ICO or IEO. This is still a very painstaking and responsible work of the project team and its advisors.
IDO startup process
IDO can be launched on decentralized exchanges such as Binance DEX, Polkastarter, and Uniswap. Moreover, such a crowdsale can be launched either completely independently or using various automation tools. The process consists of:
- Analysis. This step involves analyzing the startup in a user-friendly format. This usually means launching a website and writing a White Paper. Less commonly, startups provide MVP, product demos. In fact, the ICO algorithm is repeated.
- Drawing up an action plan for IDO. The project is sent to the launch platform of the selected DEX, where it must be checked and selected by exchange users or an external auditor. If the project is approved, it goes to the launchpad. The check is needed to protect the launchpad from junk IDO spam and scam. For example, on the Polkastarter platform, the application process is overseen by the Polkastarter team and supervisory board, which includes members from Huobi, Polygon, Alchemy, and other investors. But there are also IDO launchpads where no one checks the project.
- Presale. Initially, liquidity is replenished with financial resources from early-stage sponsors and venture capitalists investing in the market making of the liquidity pool. They are offered to buy new tokens at a large discount. Further, private investors with average investment amounts are admitted. To participate in this phase, you usually need to register with a whitelist and subscribe to the project’s social networks.
- Public sale. Tokens are sold in this phase to everyone who did not get into the whitelist, but with a smaller discount. At the same time, unlike ICOs, where the attracted capital was almost always ETH or BTC, in IDO capital, is attracted through a combination of ETH and stable coins (USDC, USDT and DAI). The public token sale itself is usually carried out in one of two ways: a) The issuer sells in batches, increasing the price of tokens at each next step. This approach attracts more attention of private small investors, since the very first buyers can get tokens with large discounts.
B) Instead of selling tokens at fixed prices, the issuer holds an auction, as a result of which the sale price is determined by supply and demand - Listing of tokens on the crypto exchange. After the successful completion of the IDO and the TGE, the token is listed for trading on the automated market maker (AMM) based DEX such as Uniswap, Pancakeswap, or Balancer. And since these are decentralized trading platforms, the listing of new tokens does not require any additional fees and permits. The issuer simply needs to create a pool of liquidity using its tokens and funds from the IDO (or other sources). In this way, the issuer will launch a liquid secondary market for its token.
- Stimulating liquidity. Some projects, after listing their token, create incentives to attract people to their ecosystem. In the most popular form, these are special programs that allow users to earn tokens by performing certain actions, for example, becoming a liquidity provider and/or a system validator. The last stage is the most problematic since incentives at any time can turn into a sale of tokens obtained in this way.
IDO pros and cons
IDO pros:
- Just organize the process. Almost any startup can raise additional funding with IDO. The absence of strict verification procedures, as under STO and IEO, has provided widespread access to IDO, which makes the tool more competitive and, at the same time, open to innovation. True, this can also be a disadvantage.
- Fast listing on exchanges. Unlike IEO/STO, IDO does not have to wait long for tokens to be listed on exchanges. Listing occurs as soon as the IDO ends. At the same time, it does not impose an obligation on the issuer to sell its tokens on only one exchange, as in the case of IEO.
- Accessibility for non-accredited investors. After regulators entered the crypto market, they demanded that only accredited investors take part in investing. IDO does not have such restrictions, which makes them available to everyone. So, at their own decision — small investors can use it.
- Reduced fundraising costs. Listing on medium to large CEX costs a lot of money today. Plus, trading platforms conduct strict due diligence on new projects, refusing them for a variety of reasons. When launching a project through IDO, this is not the case. The token will be listed almost immediately after the sale ends. Smart contracts are responsible for this, not people or CEX boards.
- Transparency. This condition is not new or unique in the world of crypto. But it’s still nice to know that you can always check the IDO smart contracts yourself and adjust your plans.
IDO cons:
- Fraud. As mentioned above, the availability of IDO is not only a plus but also a minus. Since this opens up the possibility of launching scam projects that can flood this market, as it was with ICO.
- Price jumps at the start of IDO. This model works in such a way that after the first person buys a token, its rate begins to rise. And the greater the demand at the start, the higher the dynamics. Because of this, only a few investors can purchase a token at the initial price before its value increases.
- Dumping tokens immediately after IDO. If a large number of token holders from different bounty and airdrops will have the chance to sell, for sure, such not even investors, but lovers of freebies, will always immediately dump their tokens in order to monetize at least something, which will rapidly negatively affect quotes.
- Possibility for price manipulation. Another disadvantage of the IDO is the Pump and Dump vulnerability. Some traders can use a trading bot to buy a large number of tokens at the start at a basic cost and sell them sharply when the rate rises enough. Today this is constantly happening, and so far, projects cannot control who takes part in the manipulation of their liquidity pool due to the decentralization of the process.
As in ICO, STO, and IEO, in IDO, one of the factors of success will be only the quality of the project and the professionalism of the team. Moreover, the quality of the product is now often more important than marketing, since it is easier for advertisements to rely on the quality of the product, rather than on the stories about the possible future product. If you have an MVP or demo version and it really solves some problems of users, then its IDO will undoubtedly attract the attention of investors of different levels. IDO emerged as a solution to the main problems of ICOs, STOs, and IEOs. Due to its decentralization, availability, lack of fees, and commissions, the new fundraising model in crypto can become a solution in the crypto market. But only if IDO manages to solve several important problems associated with ensuring equal access to sales for large and small investors and protection against pump and dump schemes. If these things are resolved, then IDO may become an even more popular tool in the future.
IDO perspectives
The evolution of fundraising and token launch mechanisms over the past years is a testament to how much innovation is currently taking place in the Ethereum and other crypto ecosystems. In addition, modern projects can combine the mechanics of launching and distributing their tokens. However, these mechanisms are only a means, and the final result depends on the quality of the project product itself and the competent formation of the liquidity pool. Funds are attracted using smart contracts of liquidity pools — collective repositories of funds of users of DEX platforms. In CEX, trading takes place on the basis of the order book, where orders to buy and sell assets are collected. Their price is determined by supply and demand. If users cannot agree on the price of a digital asset (there are no buyers or sellers for the quoted prices), then the market maker steps in. A CEX cannot work without a market maker — it is illiquid, and the closure of transactions would be for hours.
DEX has no order book or market makers. Their function is performed by liquidity pools — they work as automated market makers (AMM), exchanging assets without the participation of a market maker. This allows traders to exchange assets directly from the pool without waiting for buyers or sellers. The specific exchange price is set by a complex pricing algorithm called Bonding Curves. It is based on the ratio of assets in the pool: when tokens are bought, their price rises, and when they are sold, their price falls. The price balance is maintained by traders. They “freeze” their assets in the pool, providing liquidity, receiving a reward for it. At the same time, the price of an asset in a pool may differ from prices on centralized exchanges. Any DEX user can formally conduct an IDO. You just need to activate a special contract, register a new token and provide liquidity to the pool. The success of projects still depends on a committed community, a thoughtful tokenomics, a top-notch team, and a focused development strategy. Liquidity pool-based platforms such as Uniswap are increasingly becoming the preferred platform for fundraising and distribution of DeFi tokens. IDOs are gaining in popularity and are likely to become the new industry standard. Now, mainly through IDO, DeFi projects are raising funds. But this does not mean that projects from other areas of the crypto sector cannot use this funding model. However, it is unlikely that IDOs will completely replace ICOs, STOs, and IEOs.
Sergey Golubev (Сергей Голубев)
Crynet Marketing Solutions, vtorov.tech, EU structural funds, ICO/STO/IEO projects, NGO & investment projects, project management
Check out our new platform 👉 https://thecapital.io/
https://twitter.com/thecapital_io
The Evolution of Crypto Fundraising: IDO as an Alternative? was originally published in The Capital on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
